A computer network is a digital telecommunications network which allows nodes to share resources. Computers on a network are called nodes or we can say A network is defined as a group of two or more computer systems linked together.To communicate with other computer or node through network it uses different protocol.
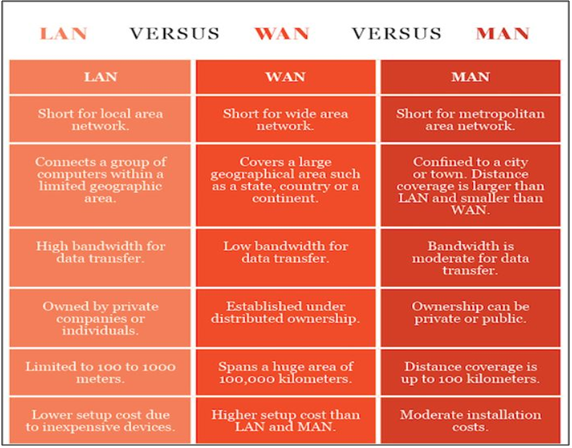
Clients and servers—how services such as e-mail and web pages connect using networks.IP addresses—how devices on a network can be found.Network hubs, switches and cables—the hardware building blocks of any network.Routers and firewalls—how to organize and control the flow of traffic on a network.
Penetration testing is a process of testing network for its security vulnerabilities. In this post we want to give you the clear image about network penetration testing stages,First directly going to penetration testing take few minutes to understand the network infrastructure or the way network work in IT sector.
We can say a network, in computing, is a group of two or more devices that can communicate. In practice, a network is comprised of a number of different computer systems connected by physical and/or wireless connections. The scale can range from a single PC sharing out basic peripherals to massive data centers located around the World, to the Internet itself. Regardless of scope, all networks allow computers and/or individuals to share information and resources.
Computer networks serve a number of purposes, some of which include:
The above information tells us that what is network and how we use it in our daily routine but there is a proper way which network follow which we can call OSI model
The network follows proper standardize communication which is known as OSI model of network.
Many applications such as email, the Web, and instant messaging rely on networking. Each of these applications relies on a particular network protocol, but each protocol uses the same general network transport methods. Many people don’t realize that there are vulnerabilities in the networking protocols themselves.
When two computers talk to each other, they need to speak the same language. The structure of this language is described in layers by the OSI model. The OSI model provides standards that allow hardware, such as routers and firewalls, to focus on one particular aspect of communication that applies to them and ignore others.
Short information on OSI model
The Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Model is a conceptual and logical layout that defines network communication used by systems open to interconnection and communication with other systems.
The model is broken into seven subcomponents, or layers, each of which represents a conceptual collection of services provided to the layers above and below it. The OSI Model also defines a logical network and effectively describes computer packet transfer by using different layer protocols.
The OSI Model may also be referred to as the seven-layer OSI Model or the seven-layer model.
When data is communicated through these protocol layers, it’s sent in small pieces called packets. Each packet contains implementations of these protocol layers. Starting from the application layer, the packet wraps the presentation layer around that data, which wraps the session layer, which wraps the transport layer, and so forth. This process is called encapsulation.
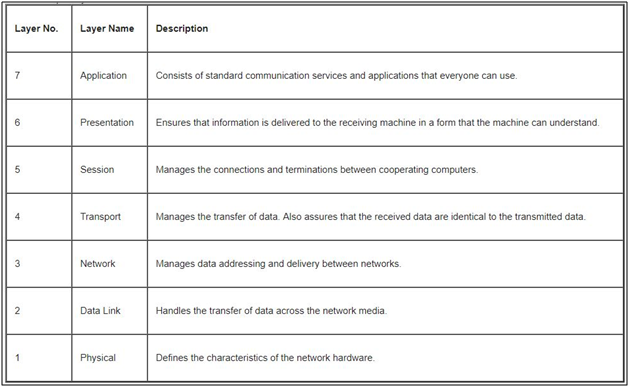
In the above information you will get the idea about how different layer use in network for communication, then we will jump to network infrastructure in this you get information on network devices and some network protocol.
Network infrastructure is the hardware and software resources of an entire network that enable network connectivity, communication, operations and management of an enterprise network. It provides the communication path and services between users, processes, applications, services and external networks/the internet. The entire network infrastructure is interconnected, and can be used for internal communications, external communications or both.
A typical network infrastructure includes:
NETWORKING HARDWARE :
NETWORKING SOFTWARE :
NETWORKING SERVICES :
It is a digital language through which we communicate with others on the Internet. protocol meaning is that it a set of mutually accepted and implemented rules at both ends of the communications channel for the proper exchange of information. By adopting these rules, two devices can communicate with each other and can interchange information. We can't even think of using the Internet without Protocols. Each protocol is defined in different terms and different use with unique name. Message travel from sender to receiver via a medium (The medium is the physical path over which a message travels) using a protocol.Or in simple ways we can say protocol is set of instruction through computer communicate in network.Each of it has its own access method of exchanging data over a computer network, such as LAN, Internet, Intranet, etc. One of the most common and known protocol examples is HTTP, that is used over the world wide web(www).
DIFFEREENT TYPES OF NETWORK PROTOCOL :
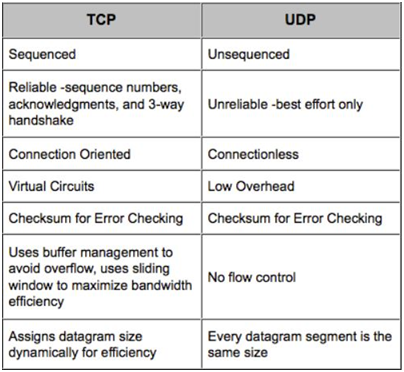
TCP works with the Internet Protocol (IP), which defines how computers send packets of data to each other. Together, TCP and IP are the basic rules defining the Internet.
User Datagram Protocol (UDP) is part of the Internet Protocol suite used by programs running on different computers on a network. UDP is used to send short messages called datagrams but overall, it is an unreliable, connectionless protocol.
In todays time all the network system usestcpip protocol because it is more secure and reliable.
How TCP work:
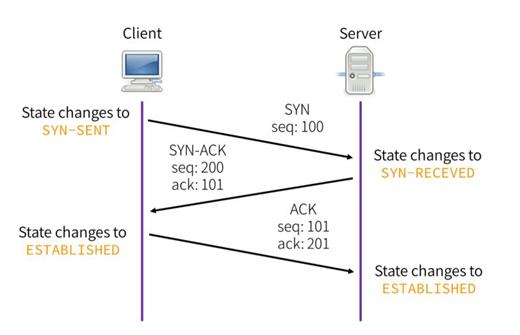
TCP use three-way handshake protocol.
Simple difference between TCP and UDP
PORTS
The door through which data can be transmitted.
Total port count is 65535.There are two types of ports
DIFFERENT TYPE OF VIRTUAL PORT :
Now the main testing part start hope you have slightly idea about what is network and how the network works. What are the different sectors we should know before starting the network pen testing?
The penetration testing it is the process to identify security vulnerabilities in an application by evaluating the system or network with various malicious techniques. the weak points of a system are exploited in this process through an authorized simulated attack. The purpose of this test is to secure important data from outsiders like hackers who can have unauthorizes access to the system. Once the vulnerability is identified it is used to exploit the system in order to gain access to sensitive information.
Before starting any testing we should know the cause of vulnerability:
CAUSES OF VULNERABILITIES
The first phase of penetration testing is information gathering. In penetration testinggathering as much information about our target is the first step.Information gathering or foot printing is of two types namely passive reconnaissance and active reconnaissance.
PASSIVE RECONNAISSANCE
In passive reconnaissance we gather information without actually interacting with the target systems.Gathering publicly available information about a company from the internet is passive reconnaissance.
ACTIVE RECONNAISSANCE
Whereas active reconnaissance requires interaction with target’s systems.Port scanning is an example of active reconnaissance.Although there are no hard and fast rules in penetration testing but it is recommended to follow a certain methodology.
You might find similarity in between network and web foot printing
Following are the different factor on which we should gatherinformation
The workflow for the network enumeration or gathering information:
| Step | Title |
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Information gathering | Passive | |
| 2 | Determining network range | Passive | |
| 3 | Identify active machines | Active | |
| 4 | Finding open ports | Active | |
| 5 | OS fingerprinting | Active/Passive | |
| 6 | Fingerprinting services | Active | |
| 7 | Mapping the network | Active |
Gathering initial information abut the target is the very first step in the foot printing process.Collecting different domain names associated with the target company, name servers, IP addresses etc is the goal here.A visit to the company’s website can provide us with a lot of useful information.Gathering initial information about the target is the very first step in the foot printing process.Collecting different domain names associated with thetarget company, name servers, IP addresses etc is the goal here.Gather the information for identifying various ways to intrude a network system.Information gathering is the main process for attacking any system.
Some of important tool for information gathering :
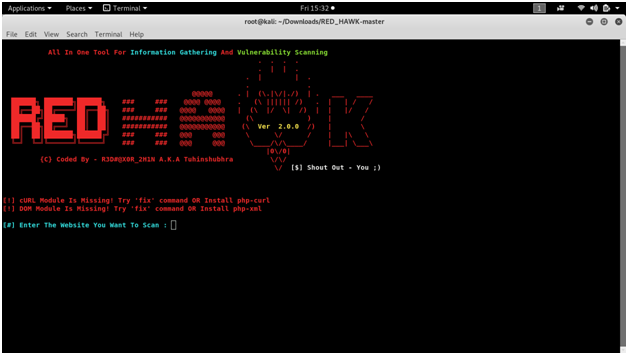
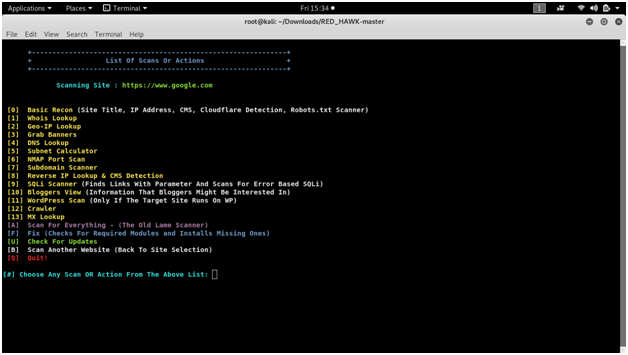
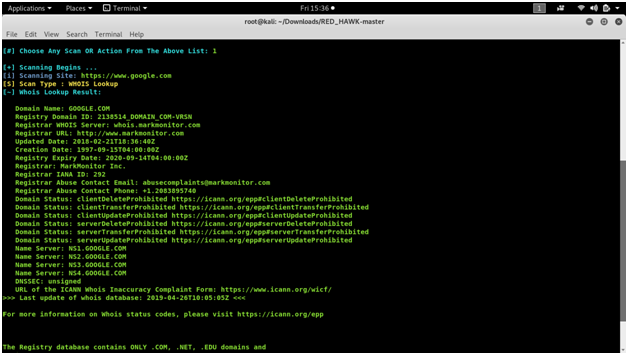
READ HAWK
vulnerability analysis with a Linux tool called Red Hawk. Recon and mapping out our target is a key step before we begin to hack or exploit anything.
Screen shots :
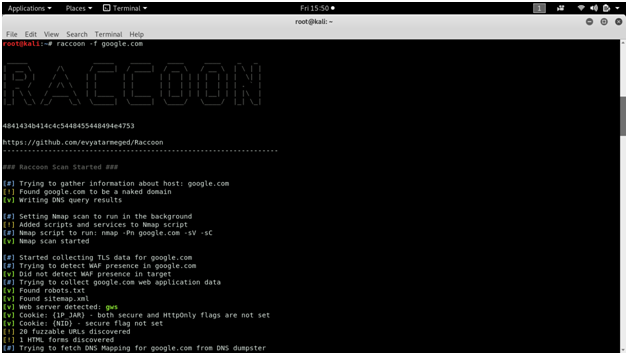
RACCOON
Raccoon is a tool made for reconnaissance and information gathering with an emphasis on simplicity. It will do everything from fetching DNS records, retrieving WHOIS information, obtaining TLS data, detecting WAF presence and up to threaded dir busting and subdomain enumeration. Every scan outputs to a corresponding file. Raccoon uses Nmap to scan ports as well as utilizes some other Nmap scripts and features.
Screen shots :
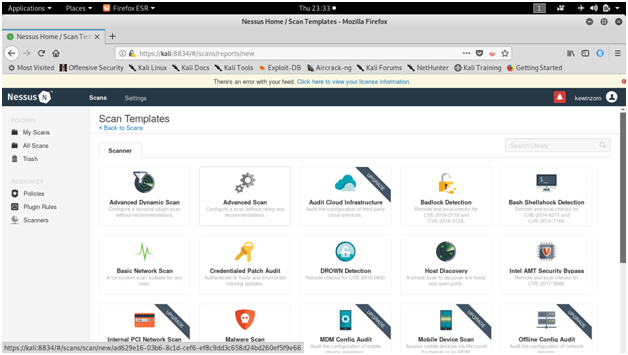
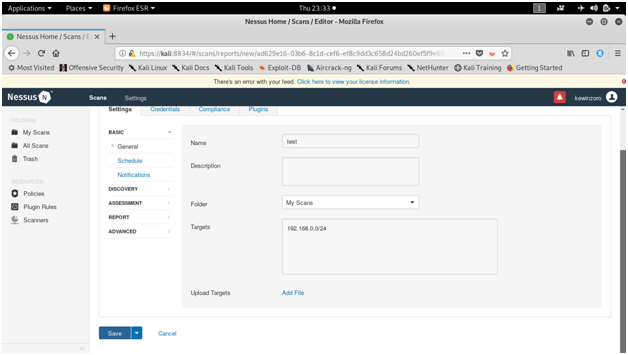
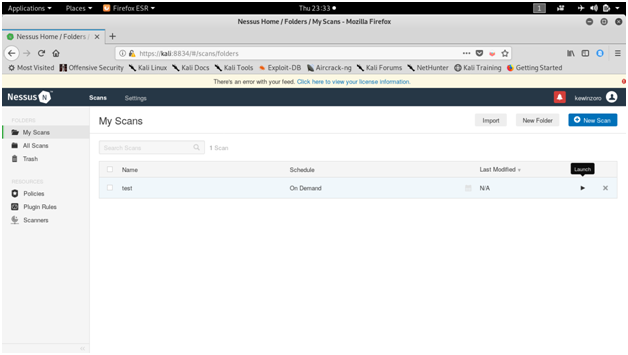
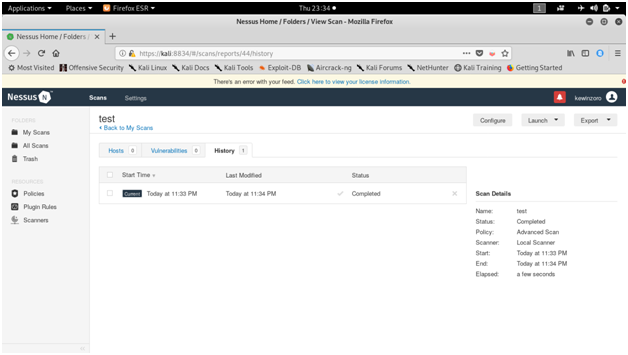
NESSUS
Tenable security’s Nessus is one of the most widely used communication vulnerability scanners, though many vendors provide comparable products. The nessus database includes vulnerabilities across platforms and protocols. Nessus has a modular architecture consisting of centralized servers that conduct scanning, and remote clients that allow for administrator interaction. Administrators can include NASL descriptions of all suspected vulnerabilities to develop customized scans.
Screen shots :
A simple ping command can help us identify the active machines but it takes a lot of timeidentifyingeach machine individually. In computing, a ping sweep is a method that can establish a range of IP addresses which map to live hosts.
BADKARMA
bad Karma is a python3 GTK+ network infrastructure penetration testing toolkit. bad Karma aim to help thetester (information gathering, vulnerabilityassessment,exploitation,post-exploitation and reporting). It allow the tester to save time by having point-and-click access to their toolkit and interacted with them through GUIs or Terminals, also every task is logged under a SQLite database in order to help during the reporting phase or in an incident response scenario.
Screen shots :
ANGRYIP
Angry IP scanner is a very fast IP address and port scanner.It can scan IP addresses in any range as well as any their ports. It is cross-platform and lightweight. Not requiring any installations, it can be freely copied and used anywhere.Angry IP scanner simply pings each IP address to check if it’s alive, then optionally it is resolving its hostname, determines the MAC address, scans ports, etc. The amount of gathered data about each host can be extended with plugins.It also has additional features, like NetBIOS information (computer name, workgroup name, and currently logged in Windows user), favorite IP address ranges, web server detection, customizable openers, etc.Scanning results can be saved to CSV, TXT, XML or IP-Port list files. With help of plugins, Angry IP Scanner can gather any information about scanned IPs. Anybody who can write Java code is able to write plugins and extend functionality of Angry IP Scanner.
Screen shots :
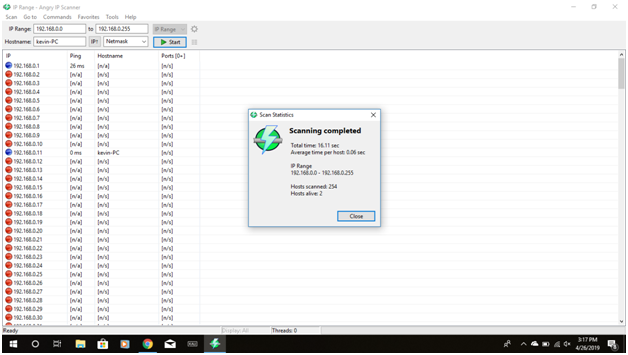
we can proceed further to identify the open ports and access points along with the OS the devices are running.The process of identification of the OS is called OS fingerprinting.
NMAP
Nmap is the most popular port scanning tool out there. It can perform a wide array of scans like TCP intense scan plus UDP port scan, TCP stealth scan, OS fingerprinting etc and can also load custom scripts.Nmap also allows us to customize the speed of the scans.
Nmap has a unique process of fingerprinting applications/devices to help us identify their communications patterns quicker.
Nmap can be used for network auditing by specifying whole subnets that you would like to scan for open/closed ports.
Nmap has a diverse presence and can be used from most operating systems.
Nmap can be used to monitor single hosts as well as vast networks that encompass hundreds of thousands of devices and multitudes of subnets.
The packets that Nmap sends out return with IP addresses and a wealth of other data, allowing you to identify all sorts of network attributes, giving you a profile or map of the network and allowing you to create a hardware and software inventory.
Screen shots :
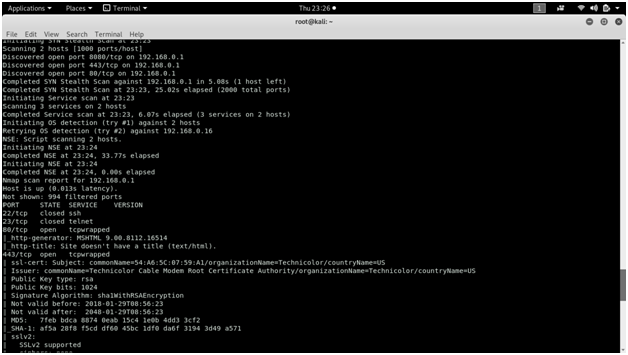
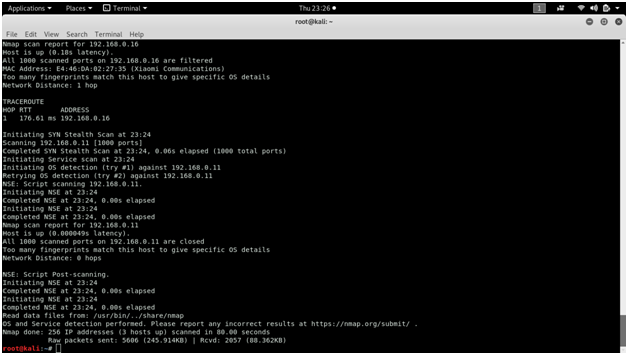
When using nmap for scanning, it displays all the open, closed or filtered ports along with the service name and protocol.
SPARTA
SPARTA is a python GUI application that simplifies network infrastructure penetration testing by aiding the penetration tester in the scanning and enumeration phase. It allows the tester to save time by having point-and-click access to their toolkit and by displaying all tool output in a convenient way.
Screen shots :
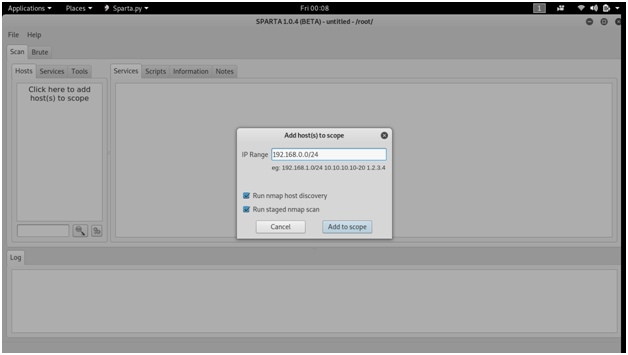
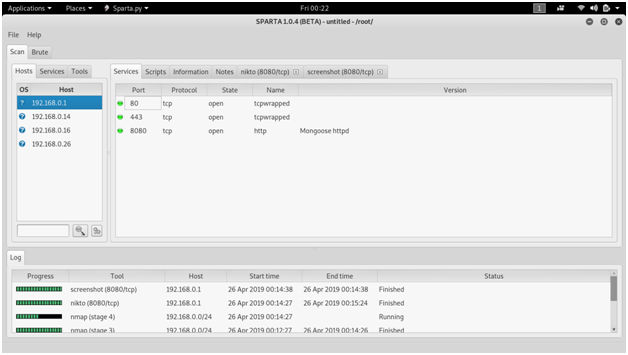
There is one more part in network penetration testing.
Network traffic capturing is another important stage for penetration testing.
Packet capture is a computer networking term for intercepting a data packet that is crossing or moving over a specific computer network.Once a packet is captured, it is stored temporarily so that it can be analyzed. The packet is inspected to help diagnose and solve network problems and determine whether network security policies are being followed.Hackers can also use packet capturing techniques to steal data that is being transmitted over a network.
The different applications and uses of data capturing include the following:
A sniffer (packet sniffer) is a tool that intercepts data flowing in a network. If computers are connected to a local area network that is not filtered or switched, the traffic can be broadcast to all computers contained in the same segment. This doesn’t generally occur, since computers are generally told to ignore all the comings and goings of traffic from other computers. However, in the case of a sniffer, all traffic is shared when the sniffer software commands the Network Interface Card (NIC) to stop ignoring the traffic. The NIC is put into promiscuous mode, and it reads communications between computers within a particular segment. This allows the sniffer to seize everything that is flowing in the network, which can lead to the unauthorized access of sensitive data. A packet sniffer can take the form of either a hardware or software solution.
A sniffer is also known as a packet analyzer.
Sniffing and monitoring the traffic is very important job in penetration testing, by doing sniffing we analyze what type of data been transfer through network. Some time we get more valuable information like user credential and password or which is the main host server and all computers are communicating with.Sniffing help you to analyze how the network is processing and it helps you for penetration testing.
Sniffing or network traffic capturing tool
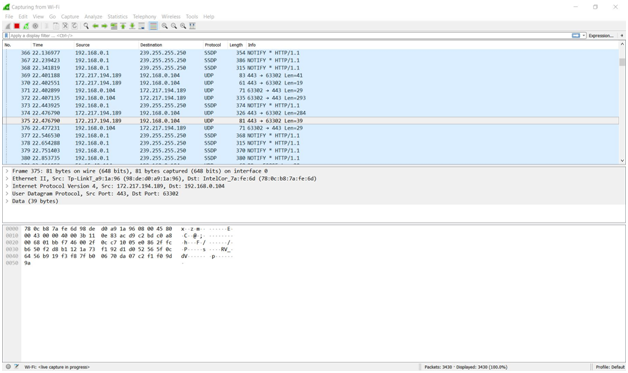
WIRESHARK
Wireshark is a free and open-source packet analyzer. It is used for network troubleshooting, analysis, software and communications protocol development, and education.
Wireshark is the world's leading network traffic analyzer, and an essential tool for any security professional or systems administrator. This free software lets you analyze network traffic in real time, and is often the best tool for troubleshooting issues on your network.
Wireshark intercepts traffic and converts that binary traffic into human-readable format. This makes it easy to identify what traffic is crossing your network.
While Wireshark supports more than two thousand network protocols, many of them esoteric, uncommon, or old, the modern security professional will find analyzing IP packets to be of most immediate usefulness. The majority of the packets on your network are likely to be TCP, UDP, and ICMP.
Screen shots :
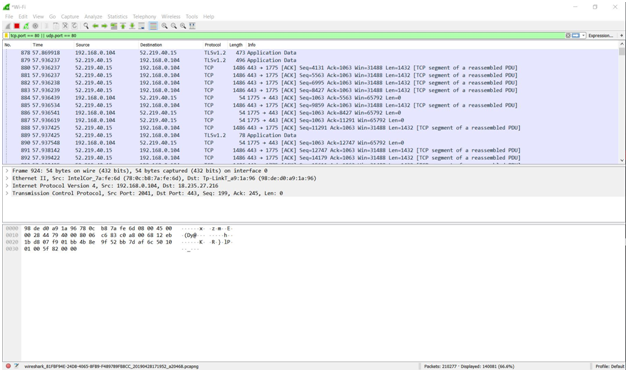
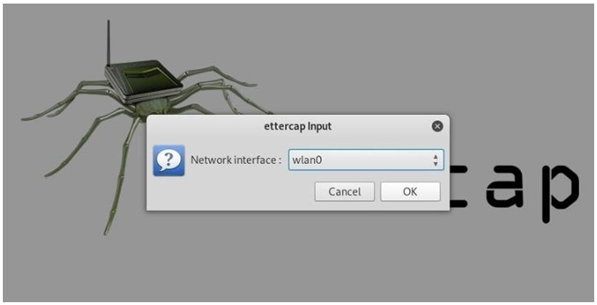
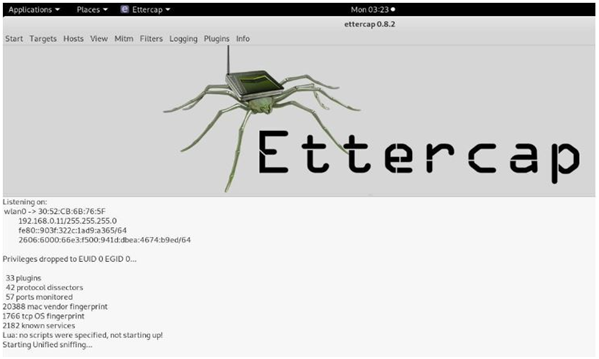
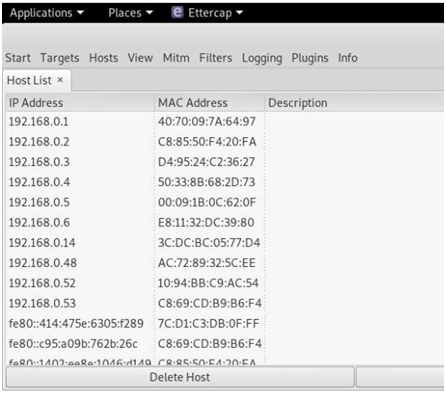
ETTERCAP
ARP spoofing is an attack against an Ethernet or Wi-Fi network to get between the router and the target user. In an ARP spoofing attack, messages meant for the target are sent to the attacker instead, allowing the attacker to spy on, deny service to, or man-in-the-middle a target. One of the most popular tools for performing this attack is Ettercap, which comes preinstalled on Kali Linux.
On a regular network, messages are routed over Ethernet or Wi-Fi by associating the MAC address of a connected device with the IP address used to identify it by the router. Usually, this happens via an address resolution protocol (ARP) message indicating which device's MAC address goes with which IP address. It lets the rest of the network know where to send traffic — but it can be easily spoofed to change the way traffic is routed.
In an ARP spoofing attack, a program like Ettercap will send spoofed messages attempting to get nearby devices to associate the hacker's MAC address with the IP address of the target.
Types of ARP Spoofing Attacks
There can be three primary outcomes after an attacker gains initial success in poisoning the ARP cache of other hosts on the network:
The major obvious limitation of ARP spoofing is that it only works if you're connected to a Wi-Fi network. This means it works on open networks but may not work well against networks that have more sophisticated monitoring or firewalls that may detect this sort of behavior.
Screen shots :